Working with Set,List,Map and Properties as attributes
 |
|
We have seen examples of having a classA as one of the attributes of another classB. We also have cases wherein the attributes of the class are a List of another object(classA).
Example File : Bill
public class Bill {
private List abc;
}
File : ABC
Public class ABC{
Private double amount;
Private double discount;
}
For such cases, the value for the List or any other similar collection needs to be injected through framework, which involves a slight syntactical change.
Step 1 :
Create the POJO which is going to be one of the attributes of another class.File : Amount.java
package com.simpleCodeStuffs;
public class Amount {
private double bill;
public double getBill() {
return bill;
}
public void setBill(double bill) {
this.bill = bill;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return("amount "+bill);
}
}
Step 2 :
CollectionBean is a class, which has a list,set,map,properties of another Object as its attributes. Just to enhance the understanding, we take it that CollectionBean may have a List of any Object as its attributes. Hence the attributes are defined as List of Object and likewise.
File : CollectionBean.java
package com.simpleCodeStuffs;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class CollectionBean {
private List stringListVariable;
private List Step 3 : Main class to print the details of the attributes
File : MainClass.java
package com.simpleCodeStuffs;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.simpleCodeStuffs.Amount;
import com.simpleCodeStuffs.CollectionBean;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
CollectionBean bean=(CollectionBean)context.getBean("testBean");
Amount amt=(Amount)context.getBean("amount");
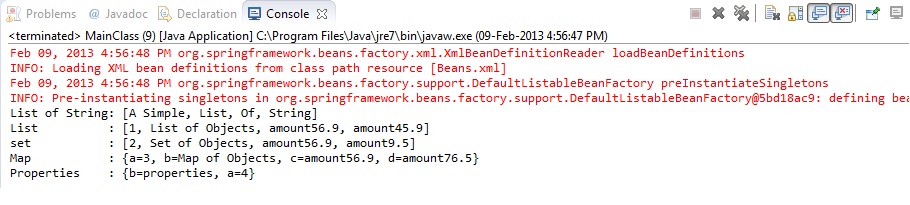
System.out.println("List of String:\t"+bean.getStringListVariable());
System.out.println("List :\t"+bean.getListVariable());
System.out.println("set :\t"+bean.getSetVariable());
System.out.println("Map :\t"+bean.getMapVariable());
System.out.println("Properties :\t"+bean.getPropVariable());
}
}Step 4 :
This is the main change. For each of the collection variables, the way in which the value is injected in the configuration metadata has a syntax change.
File : Beans.xml
A Simple List Of String 2 Set of Objects 09.5 4 properties 56.9
The first example shown, âstringListVariableâ is simply to state the means by which multiple values of a simple Data type can be injected into the list. The other variables take values of type Object. Hence, first an Integer, then a String is inserted.
The third one is to show how a reference to another bean can be inserted as a value to the list/set/map. The fourth one shows how an inner bean can be defined and the value inserted to the list/set/map. Note here that, while defining an inner bean, there is no need to mention the beanId as it has limited scope to only the outer bean which defines it.
Step 5 : Run the application. The output appears as :-
 |
|
