Constructor injection – ambiguities

 |
|
We are familiar ambiguities that may arise due to parameter type mismatch while making a call to a simple method in java. Similarly, care needs to be taken while passing values to a class using constructor injection. What about classes that contain multiple constructors with ambiguous , partially compatible dataTypes. Which exact parameters are about to match the provided constructor definition needs to be clear.
While injecting values to the properties of a bean through constructor injection, we need to make sure that the values are set as intended, on the right properties. Let us take an example.
Step 1 : Create the POJO
File : InjectionAmbiguity
package com.simpleCodeStuffs;
public class InjectionAmbiguity {
private String name;
private String score;
private int age;
//constructor 1
public InjectionAmbiguity(String name, String score,int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.score=score;
}
//constructor 2
public InjectionAmbiguity(String name, int age, String score){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.score=score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(String score) {
this.score = score;
}
}
Step 2 : Provide the Bean definition in the xml file
File : Beans.xml
Sandy 200 22
Note :
Here I have simply assumed that the 3 property values will get set in the order they are passed to the constructor. i.e., name,Score,Age and hence constructor 1 will get called.
Step 3: Create the Main Class
File : MainClass.java
package com.simpleCodeStuffs;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
InjectionAmbiguity amb=(InjectionAmbiguity)context.getBean("ambiguity");
System.out.println("name "+amb.getName());
System.out.println("Age "+amb.getAge());
System.out.println("Score "+amb.getScore());
}
}
Step 4 : Lets check if the output is as expected
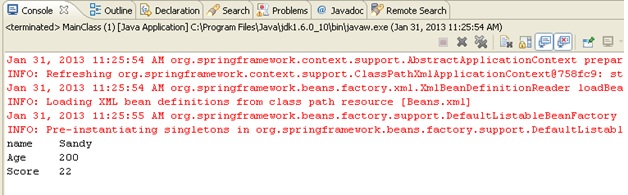
Oopsies !!!! This is because, the constructor-arg value has been passed as
200
This value has been converted from String to int and hence constructor 2 was called.
Step 5 :
To avoid such unexpected results, it is always better to make the constructor-arg injection as clear as possible. The use of type is adviced.
Beans.xml
Sandy 200 22
Now, the output is –
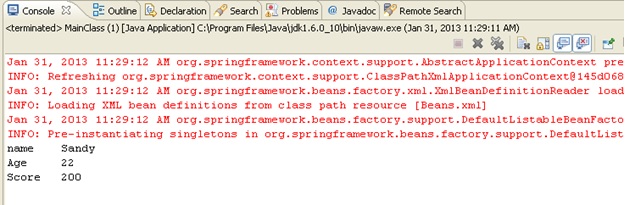
Hence the ambiguity in the parameter is resolved using more specific attributes alone with the ‘property’ tag like type to specify the intended data type of the value.
 |
|
