Model 1 and Model 2 (MVC) Architecture
Misconceptions
Student: Master, what is the difference between MVC 1 and MVC 2 ?
Master: Grasshopper, there is no such thing as MVC 1 and MVC 2, there’s just MVC. if you meant to ask about the difference between Model 1 and Model 2 with respect to web applications, then this article will help you out.
In Java there are two types of programming models
- Model 1 Architecture
- Model 2 (MVC) Architecture
** UPDATE: Struts 2 Complete tutorial now available here.
Model 1 Architecture

Flow of the Model 1 architecture.
- Browser sends request for the JSP page
- JSP accesses Business service Bean class and invokes business logic
- Business service Bean class connects to the database to store/retrieve data
- Response generated by JSP is sent to the browser
Disadvantage
Navigation control is decentralized
Model 2 (MVC) Architecture

Model 2 is based on the MVC (Model View Controller) design pattern.
- Model – Represents the data and business logic of the application.
- View – Represents the presentation.
- Controller – The controller module acts as an interface between view and model.
It intercepts all the requests i.e. receives input and commands to Model / View to change accordingly.
Advantage of Model 2 (MVC) Architecture
- Navigation control is centralized (Controller only has the control to determine the next page)
- Easy to maintain, extend and test.
Disadvantage of Model 2 (MVC) Architecture
If we change the controller code, we need to recompile the class and redeploy the application.
Autocomplete in java web application using Jquery and JSON
This article will describe how to implement jQuery Autocomplete in java web application. jQuery Autcomplete is part of the jQuery UI library which allows converting a normal textbox into an autocompleter textbox by providing a data source for the autocompleter values.

Here when user types a character in text box ,jQuery will fire an ajax request using autocomplete plugin to the controller, this controller(Servlet) in turn call the dao class which connects to the database and returns the required data back as an array list. After getting the data we convert this list to json format and return it back to the success function of our ajax call.

Library
gson-2.2.2.jar
ojdbc14.jar
servlet-api.jar
jquery-1.10.2.js
jquery-ui.js
jquery-ui.css
Project Structure
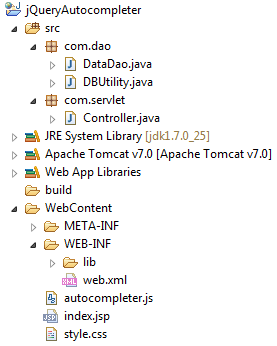
Jsp page
Now create a jsp page with Autocompleter feature and make sure that you referred the jQuery core and jQueryUI libraries.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1"> <title>Autocomplete in java web application using Jquery and JSON</title> <script src="//code.jquery.com/jquery-1.10.2.js"></script> <script src="//code.jquery.com/ui/1.10.4/jquery-ui.js"></script> <script src="autocompleter.js"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="//code.jquery.com/ui/1.10.4/themes/smoothness/jquery-ui.css"> <!-- User defied css --> <link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css"> </head> <body> <div class="header"> <h3>Autocomplete in java web application using Jquery and JSON</h3> </div> <br /> <br /> <div class="search-container"> <div class="ui-widget"> <input type="text" id="search" name="search" class="search" /> </div> </div> </body> </html>
Recommended reading:
Js file
File: autocompleter.js
In this file we get data from database via ajax and apply autocompleter
$(document).ready(function() {
$(function() {
$("#search").autocomplete({
source : function(request, response) {
$.ajax({
url : "SearchController",
type : "GET",
data : {
term : request.term
},
dataType : "json",
success : function(data) {
response(data);
}
});
}
});
});
});
When a user types a character in text box ,jQuery will fire an ajax request to the controller, in this case controller is SearchController as mentioned in the above js file.
Controller
Creating The Controller To Handle Ajax Calls
package com.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.dao.DataDao;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Controller extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("application/json");
try {
String term = request.getParameter("term");
System.out.println("Data from ajax call " + term);
DataDao dataDao = new DataDao();
ArrayList<String> list = dataDao.getFrameWork(term);
String searchList = new Gson().toJson(list);
response.getWriter().write(searchList);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
This servlet will call the business class which in turn creates the necessary connection and returns the data back as an array list to the controller. After getting the data we convert it to json format and return it back to the success function of our ajax call.
Do read
Business class
Creating Methods To Get Data From Database
package com.dao;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class DataDao {
private Connection connection;
public DataDao() throws Exception {
connection = DBUtility.getConnection();
}
public ArrayList<String> getFrameWork(String frameWork) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
PreparedStatement ps = null;
String data;
try {
ps = connection.prepareStatement("SELECT * FROM JAVA_FRAMEWORK WHERE FRAMEWORK LIKE ?");
ps.setString(1, frameWork + "%");
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
data = rs.getString("FRAMEWORK");
list.add(data);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
return list;
}
}
Data Access object
Connecting To Database Using JDBC
package com.dao;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
public class DBUtility {
private static Connection connection = null;
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
if (connection != null)
return connection;
else {
// Store the database URL in a string
String serverName = "127.0.0.1";
String portNumber = "1521";
String sid = "XE";
String dbUrl = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@" + serverName + ":" + portNumber
+ ":" + sid;
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
// set the url, username and password for the databse
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(dbUrl, "system", "admin");
return connection;
}
}
}
web.xml
Make sure you have done servlet mapping properly in web.xml file. An example of this is given below,
<welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <servlet> <servlet-name>SearchController</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.servlet.Controller</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>SearchController</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/SearchController</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
Demo

Concept of Servlets Vs Concept of Struts 2
In our previous article we have created a hello world program in struts2, in which I have passed parameter from request and setted in action class via a member variable, which may led you in some confusion, since in case of servlets the member variable in it are shared between all request and only those variable inside doget and dopost methods remains unique. So inorder to know why a member variable in struts 2 remains unique per request, we have look into the conceptual difference between Servlets and Struts 2. This article deals with the same.

** UPDATE: Struts 2 Complete tutorial now available here.
In case of Servlet when we have N number of request then only one object is created out of which N number of Threads are created , in which a request object is created. So the objects inside the thread are safe and not shared with other thread objects.
But suppose if the Servlet has Member variable, then those variable are not thread safe, as they are shared between all the threads created for each request.
The above concept is depicted pictographically below.

Note: Servlet & Struts 1 follows same concept.
In case of struts 2 for N number of request N number of object is created. So in this case, even the member variable for these objects are not shared between objects of other request, that the reason Struts 2 is said to be thread safe.
The concept of Struts 2 is depicted pictographically as below.

In our next article we shall learn about the roles of Action class in struts 2.
Export Grid View to Excel in Servlet and Jsp
Exporting contents to excel spreadsheet is a much required functionality for almost every data driven website. In this article I am going to explain in detail on how to export gridview contents to an excel sheet via a java web application.
Project Structure

Servlet
package servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import model.Student;
public class ExportToExcel extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();
students.add(new Student("Mohaideen", "CSE", 17));
students.add(new Student("Nilafar", "IT", 16));
students.add(new Student("Thasleema", "CSE", 16));
request.setAttribute("students", students);
RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher("report.jsp");
rd.forward(request, response);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();
students.add(new Student("Mohaideen", "CSE", 17));
students.add(new Student("Nilafar", "IT", 16));
students.add(new Student("Thasleema", "CSE", 16));
request.setAttribute("students", students);
RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher("exportExcel.jsp");
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
Model
package model;
public class Student {
private String name;
private String department;
private int age;
public Student(String name, String department, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.department = department;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setDepartment(String department) {
this.department = department;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
JSP Page
File : index.jsp – Used to navigate to exporttoexcel servlet action
<html> <head> <META HTTP-EQUIV="Refresh" CONTENT="0;URL=exporttoexcel"> </head> <body> </body> </html>
File : report.jsp – This page used to display gridview filled with data of student table from server side.
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ page import="java.util.List"%>
<%@ page import="model.Student"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Export to Excel</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Export to Excel Example</h3>
<form action="exporttoexcel" method="post">
<table cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" border="1" bordercolor="gray">
<tr>
<td><b>Name</b></td>
<td><b>Department</b></td>
<td><b>Age</b></td>
</tr>
<%
List<Student> students = (List<Student>) request
.getAttribute("students");
for (Student std : students) {
%>
<tr>
<td><%=std.getName()%></td>
<td><%=std.getDepartment()%></td>
<td><%=std.getAge()%></td>
</tr>
<%
}
%>
</table>
<BR /> <input type="submit" value="Export To Excel" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
File : exportExcel.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ page import="java.util.List"%>
<%@ page import="model.Student"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Export to Excel Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Export to Excel Example</h3>
<table cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" border="1" bordercolor="gray">
<tr>
<td>Name</td>
<td>Department</td>
<td>Age</td>
</tr>
<%
List<Student> students = (List<Student>) request.getAttribute("students");
if (students != null) {
response.setContentType("application/vnd.ms-excel");
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "inline; filename="
+ "StudentReport.xls");
}
for (Student std : students) {
%>
<tr>
<td><%=std.getName()%></td>
<td><%=std.getDepartment()%></td>
<td><%=std.getAge()%></td>
</tr>
<%
}
%>
</table>
</body>
</html>
web.xml
<web-app .. version="3.0">
<display-name>ExportToExcel</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ExportToExcel</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>servlet.ExportToExcel</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ExportToExcel</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/exporttoexcel</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Demo
On running the application

On clicking “Export To Excel” button the following page with download file options get appears

Servlet + Jsp Hello World Example
In our previous tutorial we got introduced to what a JSP is, In this article we are going to cover how to write Hello world example using both Servlet and Jsp.
Final Project Structure

Servlet
package com.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class HelloWorldServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher("hello.jsp");
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
web.xml
Make sure that your web.xml file has following mapping
<web-app ..> <display-name>HelloWorldServlet</display-name> <servlet> <servlet-name>HelloWorld</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.servlet.HelloWorldServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>HelloWorld</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/helloworld</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
JSP Page
<html> <head> <title>Hello world in Servlet + JSP</title> </head> <body> <p>Hurray!! This Servlet worked!!!</p> </body> </html>
Demo
Deploy the application tomcat server and enter the URL to access HelloWorldServlet “http://localhost:8089/HelloWorldServlet/helloworld”

Why use JSP when we can do the same thing with servlets?
Highly Coupled Servlets
In our previous tutorial we have implemented an servlet hello world example, in which a servlet acts as both controller as well as presenter; below are the list of problem when servlet acts as both controller and presenter,
- High cost of maintenance
- HTML and Java exist in the same file.
- Web Designers don’t understand java code, don’t like the java code…
- Programmers don’t particularly like the messing with <HTML> code!!!!
In simple words ….
if( developer == javaProgrammer)
System.out.println("Stick to Java code!");
else if( developer == webDesigner )
System.out.println("Stick to html code!");
So its better to separate JAVA code from the HTML code. Now the Question is How to Separate ????
Java Server Pages(JSP)
Java Server Pages (JSPs) provide a way to separate the generation of dynamic content (java) from its presentation (html)
How do JSP’s Work
The work flow of jsp is depicted pictographically below.
In our next tutorial we shall learn to implement hello world example in servlet using JSP.

