How To Create Linear Layout in an Android Application using Eclipse

In this Tutorial, you will Learn
1.How to display an activity in Linear layout
2.What are the various types of linear layouts available
Before creating an android application using Eclipse, let us see some of the key terms involved while developing this application.
Key terms involved in this project:
Layout: A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget. You can declare a layout in two ways:
- Declare UI elements in XML
- Instantiate layout elements at runtime.
Linear Layout: Linear Layout is a view group that aligns all children in a single direction, vertically or horizontally. You can specify the layout direction with the android:orientation attribute. All children of a Linear Layout are stacked one after the other, so that a vertical list will only have one child per row, no matter how wide they are, and a horizontal list will only be one row high (the height of the tallest child, plus padding). A Linear Layout respects margins between children and the gravity (right, center, or left alignment) of each child.
** UPDATE: Android Complete tutorial now available here.
Layout Weight: Linear Layout also supports assigning a weight to individual children with the android:layout_weight attribute. This attribute assigns an “importance” value to a view in terms of how much space is should occupy on the screen. A larger weight value allows it to expand to fill any remaining space in the parent view.
The tutorial is about how to display an activity in linear layout(both horizontal and vertical).
This project is developed in Eclipse 4.2 (Juno) and tested with Android 2.2
If you are new to new to android application project, to create a new project in Eclipse refer Creation of Android Project.
Coding:
Now let’s go to the coding section. This project requires following files.
Source Code:
- Linearlayout.java (Activity in horizontal linearlayout)
- Verticallayout.java (Activity in vertical linearlayout)
Activity Files:
- activity_linearlayout.xml – horizontal linearlayout activity
- activity_verticallayout.xml – vertical linearlayout activity
res – Values:
- strings.xml – strings available in both horizontal and vertical layouts
Manifest file:
- AndroidManifest.xml - common to both horizontal and vertical layouts
Here are the coding for the above files.
Linearlayout.java:
package com.example.linearlayout; // Linearlayout package for horizontal layout
import android.os.Bundle; // A mapping from String values to various Parcelable types.
import android.app.Activity; // Required to create an activity.
import android.view.Menu; // Interface for managing the items in a menu.
public class Linearlayout extends Activity { // all classes extends activity
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Create an activity/ screen
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// displays activity linearlayout in horizontal layout when app starts
setContentView(R.layout.activity_linearlayout);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { // Menu settings
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_linearlayout, menu);
return true;
}
}
activity_linearlayout.xml:
activity_verticallayout.xml:
Menu : activity_linearlayout.xml
Menu : activity_verticallayout.xml
AndroidManifest.xml:
strings.xml:
Linearlayout - Horizontal Linearlayout - Vertical Settings Settings
Styles. xml:
Run the android application:
Android applications can be run on the android devices. You can either connect a hardware to the system to test the application or you can use the android virtual devices (AVD) Manager to create/manage the virtual devices running on emulator to run the application.
If you are new to create a Android Virtual Device (AVD), refer Creating Android Virtual Device.
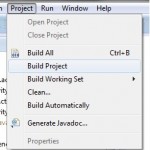
To run the application/ project, Build your project using Project ->Build Project.
This will show errors in Console window at the bottom of the working area in case your project contains.
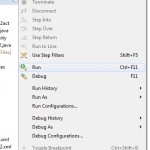
If your build is successful, Run your application using Run -> Run or Press Ctrl +F11.
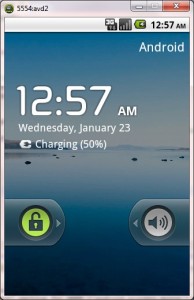
Upon running the application, the emulator will be launched which displays the AVD on your screen.
You can see your app with the image set during the android project creation in AVD.
Upon running the application, the emulator will be launched with the selected/ available AVD created on your screen.
To test your application, unlock the screen and double click on your app.
You can see your app with the image set during the android project creation in AVD.
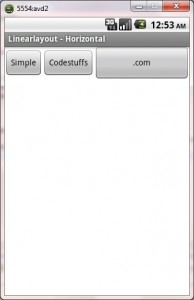
Horizontal Activity:
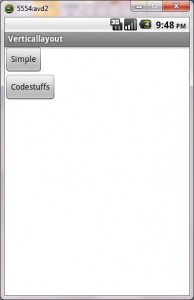
Vertical Layout:
Thus the android application project is executed successfully.